Compostable materials have garnered increasing attention and applications in the field of flexible pouch packaging due to growing environmental awareness. Compostable materials are capable of natural degradation under specific environmental conditions, unlike traditional plastics. They are typically made from biopolymers such as polylactic acid (PLA).
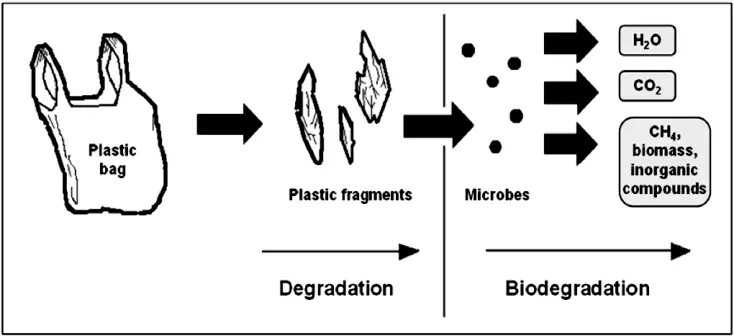
Compostable materials used in pouch packaging can be broken down by microorganisms in composting facilities, eventually transforming into organic matter, water, and carbon dioxide, thus achieving circularity.
However, it is important to note that the degradation performance of compostable materials may be limited by certain conditions. In real-world environments, compostable materials may not degrade effectively, particularly in home composting or natural environments where necessary conditions such as temperature, humidity, and microbial activity may be lacking. Therefore, the actual degradation rate may be slower than expected, limiting the potential environmental benefits.
Additionally, the production cost of compostable materials is generally higher, which may increase manufacturing costs and potentially impact profitability. Supply chain limitations, including material availability and composting facilities, also pose challenges.
While compostable materials theoretically offer environmental advantages, their practical applications require careful consideration of degradation performance, cost, and supply chain factors. The use of compostable materials may be beneficial for certain industries and products, but in other cases, alternative eco-friendly options may be more suitable.
Understanding the applications and environmental advantages of compostable materials in pouch packaging, along with acknowledging the challenges they may face, helps provide an objective assessment of their suitability and promotes the development of sustainable packaging solutions.
Post time: 07-12-2023

